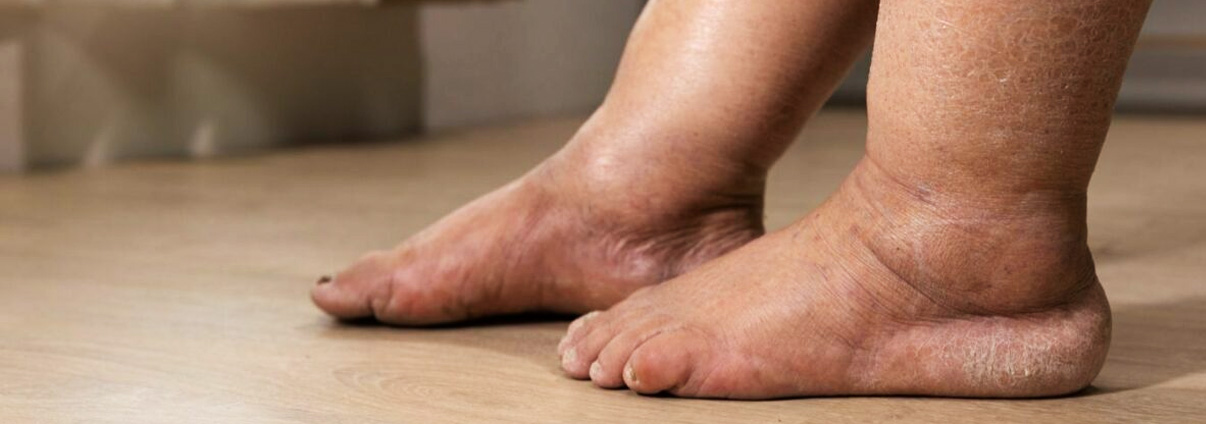
Swelling, also known as edema, occurs when fluid accumulates in the body's tissues, leading to enlargement or puffiness in the affected area. Swelling can occur in any part of the body but is most commonly observed in the extremities, such as the legs, ankles, feet, hands, and arms. It can be a result of injury, inflammation, or underlying medical conditions.
Causes
- Swelling can be caused by a variety of factors, including Injury, Infections, Inflammatory conditions like arthritis or gout can cause swelling due to inflammation of the joints.
- Chronic Medical Conditions, Heart Failure, Kidney Disease, Liver Disease.
- Poor circulation in the veins, often due to weakened vein valves, can cause blood to pool in the legs, leading to swelling.
- Lymphedema: This occurs when the lymphatic system is blocked or damaged, leading to fluid buildup and swelling, typically in the arms or legs.
- Swelling can occur as part of an allergic reaction, especially in the face, lips, and throat, which can be dangerous if it obstructs breathing.
Types of Swelling
- Localized Swelling
- Generalized Swelling
- Pitting Edema
- Non-Pitting Edema
Treatment
Treatment for swelling depends on the underlying cause and may include:
- Surgery: In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove the cause of the swelling, such as draining an abscess or repairing damaged veins.
- Rest and Elevation: Resting the affected area and elevating it above heart level can help reduce swelling, especially for injuries or venous insufficiency.
- Cold Therapy: Applying ice packs to the swollen area can reduce inflammation and pain.
- Compression: Wearing compression garments, such as stockings or sleeves, can help reduce swelling by improving circulation.
- Physical Therapy: For conditions like lymphedema, physical therapy, including specialized massage techniques and exercises, can help manage swelling.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention if swelling is accompanied by other symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or if it develops suddenly and is severe. Persistent or unexplained swelling should also be evaluated by a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.