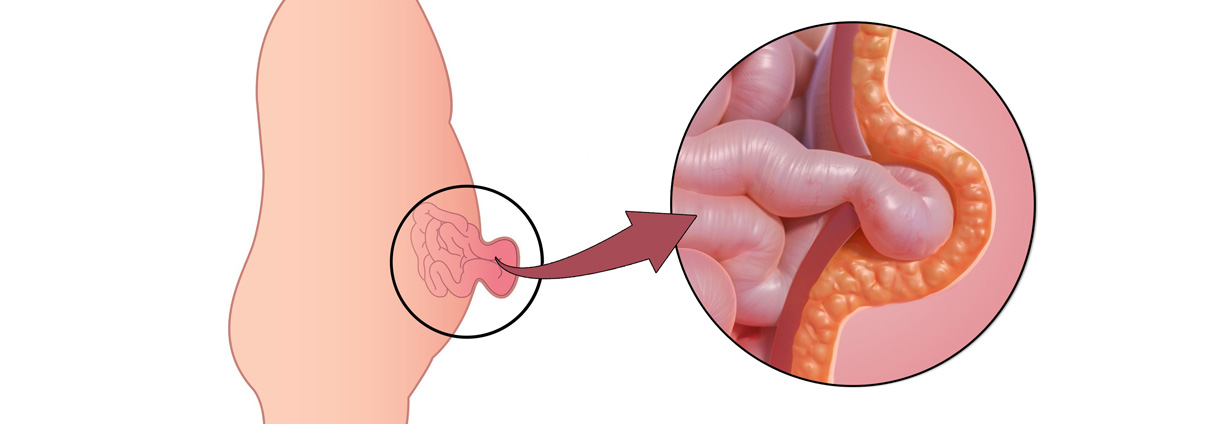
Hernia surgery is a procedure performed to repair a hernia, which occurs when an internal organ or tissue pushes through a weakened area of muscle. Common hernias include inguinal, umbilical, and hiatal hernias, each requiring different approaches depending on severity and location. The surgery aims to strengthen the weakened muscle and prevent further complications like organ obstruction or strangulation.
Types of Hernia Surgery
There are two main types of hernia surgery: open surgery and laparoscopic surgery. In open surgery, a larger incision is made to access and repair the hernia, while laparoscopic surgery uses smaller incisions and a camera to guide the surgeon. Laparoscopic surgery is less invasive, resulting in faster recovery and less postoperative pain, though not all patients are eligible for this option. Both types may use mesh to reinforce the weakened muscle area and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Recovery and Risks:
Recovery from hernia surgery varies depending on the type of procedure, but most patients can return to normal activities within a few weeks. Common risks include infection, pain, and recurrence of the hernia, though these are generally low with proper care. Surgeons may advise patients to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activity during recovery to ensure the repair heals properly and to minimize the risk of complications.