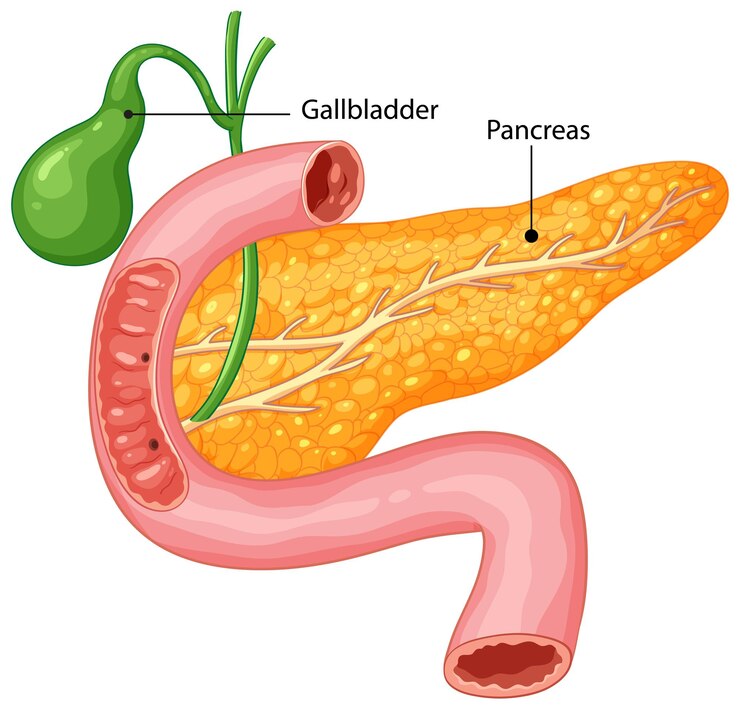
The tiny pouch known as the gallbladder serves as a storage facility for extra bile. It connects to the main bile draining ducts directly below the liver. The gallbladder contracts during eating to release bile into the intestine for fat processing.
What are gallstones?
The formation of gallstones, also known as cholelithiasis (from the Greek chol (bile)-lith (stone)-iasis (process)), is caused by cholesterol-forming gallbladder stones.
Gallstone Types
Based on the way the stone is formed, it can be divided into three main categories.
Mixed stones: A combination of salts and cholesterol results in mixed stones. These multicolored stones usually occur in clusters.
Cholesterol stones: The main component of cholesterol stones is cholesterol, a chemical that resembles fat and is necessary for many metabolic processes. If cholesterol stones get big enough, they can obstruct the bile ducts.
Pigment stones: Some pigments give bile its greenish-brown color. Bile pigment gallstones are typically small, yet they can occur in huge quantities. Reasons for Gallstones
There are numerous causes of gallstones. Gallstones are more common in women than in men.
- Those with a history of gallstones in their families.
- Obese people are more likely to get gallstones.
- In certain individuals, the liver overproduces cholesterol. This can lead to the development and growth of cholesterol crystals in the bile into stones.
- As people age, gallstones become increasingly prevalent.
Identification of gallstones
Numerous tests are used to diagnose gallstones, such as:
- General exams, such as radiography and physical examinations.
- One type of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for a body imaging technology is magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP).
- The patient had their pancreas, liver, and biliary systems imaged using an MRI machine.
- An endoscope test is called endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, or ERCP.
- A tiny tube is inserted through the oesophagus and used to inject dye into the intestines to enhance the quality of x-ray pictures.
- Ultrasound: Sound waves produce a picture that indicates the presence or absence of gallstones.
Why do stones form in the gallbladder?
For whatever reason, it seems to affect women more frequently than men, as well as individuals who take cholesterol-lowering medications, have diabetes, have a family history of gallstones, are overweight, obese, or experience fast weight loss. The frequency of gallstones rises with age.
Why is gallbladder surgery necessary for me?
You require surgery if you have symptoms. It's your body's method of alerting you to a problem with your gallbladder. Gallbladder stones without symptoms are usually not surgically removed. Certain signs precede any complications.
What factors lead to gallstones?
Why certain people acquire gallstones is unknown. Gallstones cannot be prevented in any way. But compared to men, obese, fertile women over forty are more likely to have gallstones. Hormone replacement therapy, birth control pills, or excess estrogen during pregnancy can raise bile cholesterol levels, slow down the emptying of the gall bladder, and increase the risk of gallstones. Pigment stones are more common in people with genetic blood disorders such as sickle cell anemia and hereditary spherocytosis, a condition in which an excessive amount of bilirubin is produced.
What is the gallstone treatment?
The most effective way to treat gallstones is to have the gall bladder removed during surgery. The term for this is cholecystectomy. The conventional approach to a cholecystectomy involved an extended incision made beneath the right side of the rib cage during open surgery. The procedure used nowadays to remove gallbladders is called laparoscopic surgery, or "keyhole surgery."
What advantages does a laparoscopic cholecystectomy offer?
- Only four tiny abdominal incisions are needed for the procedure, as opposed to a five to seven inch incision.
- Minimal pain following surgery
- Quicker recuperation
- A quicker return to routine tasks
- Shorter hospital stay
What safety measures need to be taken following surgery?
The comfort level of the patient usually limits the amount of activity. Within a week, patients will be able to resume their regular activities, such as driving, light lifting, and working. Following surgery, patients are encouraged to follow a modest diet for one week.